Principles Behind Remote Control Technologies — The Science Behind Wireless Control in Modern Bangladesh
Introduction
In today’s hyper-connected world, controlling devices without direct contact has become second nature. From switching on a TV using a remote to managing smart home lights in Dhaka via mobile apps, remote control technology powers our modern lifestyle.
In Bangladesh, these technologies are more than just conveniences — they’re tools for progress. From SMS-controlled irrigation systems in Rajshahi to Bluetooth-powered robotics projects in universities, remote control systems are empowering innovation and efficiency. This blog unpacks the core principles, tools, and real-world applications of remote control technologies, tailored for students, engineers, and ICT enthusiasts of Bangladesh.
Theoretical Framework: Understanding Remote Control Principles
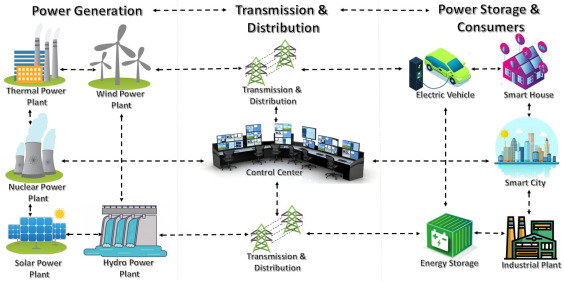
Remote control is the process of operating a device or system from a distance without direct physical contact. It functions through the transmission and reception of signals that carry instructions between a transmitter and a receiver, which then activate the target device.
Core Components
-
Transmitter: Sends the signal — e.g., a TV remote, mobile app, or drone controller.
-
Receiver: Interprets the incoming signal — e.g., infrared (IR) sensor, RF receiver, or IoT module.
-
Controlled Device: Performs the intended action — e.g., light system, motor, robot, or appliance.
Types of Remote Communication
-
Infrared (IR): Uses invisible light; short-range control (TVs, ACs).
-
Radio Frequency (RF): Includes Bluetooth and Wi-Fi; allows control through walls and over longer distances.
-
Wired Control: Used in specialized industrial environments.
-
GSM/Internet-Based Control: Enables global access through mobile networks or IoT platforms.
A vital element here is signal modulation — encoding data into signals for transmission and decoding them on the receiver’s end. This ensures accuracy and secure execution of commands.
Tools and Methods Used in Remote Control Systems
Remote control systems rely on a mix of hardware and software, customized to the purpose and range of operation.
| Tool/Module | Function | Example in Bangladesh |
|---|---|---|
| Infrared (IR) Modules | Transmit coded light pulses for simple commands | Used in TVs, fans, and AC systems |
| Bluetooth/Wi-Fi (HC-05, ESP8266) | Enable wireless smartphone-based control | Student robotics and smart home projects |
| Microcontrollers (Arduino, Raspberry Pi) | Process incoming signals and execute actions | Used in IoT and automation prototypes |
| IoT Platforms (Blynk, ThingSpeak) | Cloud-based device control and data monitoring | Smart home and agricultural automation |
| RF Modules (433 MHz) | Medium-range control via radio waves | Drones, RC cars, and alarms |
| GSM Modules (SIM800L) | SMS-based control without internet dependency | Used in rural irrigation systems |
These tools form the foundation of smart, responsive, and low-cost control systems that suit Bangladesh’s unique mix of urban and rural needs.
Applications in Bangladesh: Real-Life Impact
Remote control technologies are revolutionizing everyday life across various sectors in Bangladesh.
1. Agriculture Automation
In Rajshahi and Rangpur, farmers use GSM-based irrigation pumps controlled via SMS or calls. This minimizes labor and ensures efficient water usage, even when farmers are away from the field.
2. Smart Homes
In Dhaka and Chittagong, students and tech hobbyists create home automation systems using Arduino and Wi-Fi modules. Lights, fans, and door locks can be controlled via smartphone apps, increasing energy efficiency and convenience.
3. Robotics & Competitions
ICT Olympiad Bangladesh and university tech events feature Bluetooth and RF-controlled robots designed by students. These robots perform tasks like line-following, obstacle avoidance, and delivery, showing real-world uses of wireless control.
4. Disaster Management & Rescue
During floods and cyclones, drones and remote-controlled boats assist in rescue missions. Equipped with cameras and GPS, they can be safely operated from a distance, helping responders avoid danger zones.
Benefits of Remote Control Systems
-
⚙️ Efficiency: Reduces manual effort and operation time.
-
🔒 Safety: Minimizes human exposure to hazardous conditions.
-
💡 Innovation: Encourages students to create new ICT-based solutions.
-
🌱 Sustainability: Optimizes resource use, especially in agriculture.
-
📶 Accessibility: GSM and Wi-Fi systems enable control from anywhere.
Conclusion
Remote control technology is shaping the backbone of modern automation in Bangladesh. Whether managing home devices, operating factory machinery, or innovating in school labs, understanding its working principles empowers the next generation of problem-solvers.
As Bangladesh moves toward its Smart Bangladesh 2041 vision, the mastery of remote communication technologies will open endless opportunities in IoT, robotics, and digital innovation. For ICT Olympiad students, this topic connects theory with real-world transformation — bridging curiosity and creation.
Practice Tasks for Students
🔧 Design Challenge
Build a Bluetooth-controlled LED system using an Arduino and HC-05 module. Add features like brightness or RGB color control.
🌾 Research Task
Investigate how GSM modules are applied in remote irrigation systems in rural Bangladesh. Can you design a low-cost version?
🧠 Write & Explain
Compare Infrared (IR) and Radio Frequency (RF) communication with examples from daily life.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is remote control technology?
Remote control technology allows users to operate devices from a distance using signals like infrared, radio frequency, or mobile communication.
Q2: How do GSM modules help Bangladeshi farmers?
They enable farmers to turn water pumps on or off via SMS, reducing time and physical effort in managing irrigation.
Q3: What are the differences between IR and RF remote control?
IR works line-of-sight and short-range; RF works through obstacles and at longer distances.
Q4: How can students practice remote control projects?
By building simple Arduino or IoT projects, like Bluetooth-controlled fans or GSM-based lighting systems.
Key Takeaways
-
A remote control enables the command of devices from a distance using signals.
-
IR, RF, GSM, and IoT are the key transmission methods.
-
Bangladesh is applying these technologies in homes, farms, and factories.
-
Understanding these systems supports innovation for Smart Bangladesh 2041.