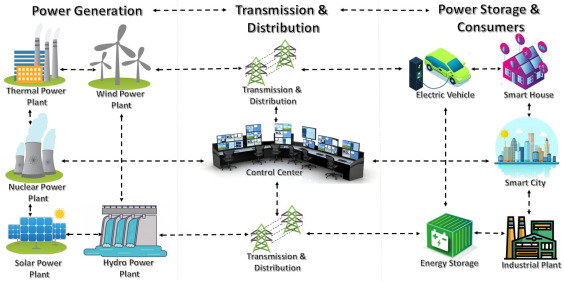
Real-Life Automation in Bangladesh: From Smart Homes to Smart Industries

Dial Chowdhury
06 November 2025 . 7 Minute Read
Introduction
Automation is no longer limited to high-tech factories — it’s now improving everyday life across Bangladesh. From automatic cutting machines in garment factories to motion-controlled lights in Dhaka apartments, automation is shaping how we live and work. As the nation moves toward its Smart Bangladesh 2041 vision, students and innovators must understand how automation operates in local contexts.
This article explores how sensors, controllers, and smart systems are already powering automation in Bangladesh’s industries, homes, and agriculture — turning ideas into action.
Theoretical Framework: Understanding Automation
Automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks with minimal human involvement. It relies on a simple yet powerful three-stage model:
-
Input: Sensors detect physical conditions such as temperature, light, or motion.
-
Processing: Controllers (e.g., microcontrollers, PLCs) analyze the sensor data and decide what action to take.
-
Output: Actuators (motors, alarms, or displays) perform the necessary response.
In Bangladesh, automation often blends Arduino, Raspberry Pi, PLC systems, Wi-Fi, GSM modules, and IoT platforms. Together, these components improve productivity, safety, and energy efficiency in both industrial and domestic settings.
Tools and Methods Used in Automation
1. Microcontrollers (Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
Used in home and small-scale industrial projects to automate lighting, temperature, and motor systems.
➡ Example: School students in Dhaka design Arduino-based automatic fans that run only when heat levels rise.
2. PLC (Programmable Logic Controller)
Essential in large-scale industries such as garments and textiles in Gazipur, Narayanganj, and Dhaka, PLCs precisely manage dyeing, cutting, and sewing processes.
3. Sensors
| Sensor Type | Function | Local Example |
|---|---|---|
| Motion Sensor | Detects movement for lights and alarms | Office corridors in Dhaka |
| Temperature Sensor | Controls smart fans/AC | Automated classrooms |
| Water Level Sensor | Prevents tank overflow | Urban apartments |
| Gas/Smoke Sensor | Enhances kitchen safety | Homes using LPG cylinders |
4. IoT Platforms and Mobile Apps
Platforms like Blynk, Thingspeak, or custom SMS systems enable remote control.
➡ Example: Farmers in Rangpur use SMS commands to start solar pumps.
5. Relay Modules and Actuators
These components switch on appliances or motors based on signals from sensors or controllers, bridging the digital and physical worlds.
Automation in Real Bangladeshi Contexts
Industrial Automation
-
Garment & Textile Industry – Dhaka, Gazipur, Narayanganj
PLC-controlled machines manage fabric cutting, dyeing, and sewing. Conveyor belts and robotic arms streamline packing. -
Food & Cold Storage – Jessore, Bogura, Dinajpur
Automated temperature and humidity systems protect produce like potatoes and mangoes from spoilage. -
Smart Irrigation – Rajshahi, Rangpur
GSM-based pumps and soil sensors automate watering, conserving energy and resources. -
Power Plants – Ashuganj, Rampal
Automated systems monitor voltage, detect faults, and ensure operational safety.
Home and Building Automation
-
Automatic Lighting & Fan Control – Dhaka, Chattogram
Motion sensors manage lights and fans to reduce electricity use. -
Voice-Activated Devices
Smart speakers (Google Home, Alexa) let users control home systems hands-free. -
Smart Locks & Security Cameras
Fingerprint and RFID systems secure urban homes and offices. -
Gas Leak Detection
IoT gas sensors alert homeowners via alarms or SMS in case of leaks.
Why Automation Matters for Bangladesh
Automation drives:
-
⚙️ Higher industrial productivity
-
💡 Energy efficiency in homes and offices
-
🌾 Sustainable farming through smart irrigation
-
🧠 STEM learning for students and innovators
It also aligns directly with the Smart Bangladesh 2041 mission — empowering citizens through innovation, connectivity, and efficiency.
Conclusion
Automation isn’t just a futuristic concept — it’s already transforming Bangladesh’s industries, farms, and homes. Affordable technologies like Arduino, IoT, and PLC systems are enabling both professionals and students to create intelligent, real-world solutions.
As Bangladesh embraces its digital transformation, learning automation opens doors to new opportunities — from factory management to smart urban living. Now is the time for students to explore, innovate, and build automation projects that contribute to a smarter, more efficient Bangladesh.
Practice Tasks for Students
-
Research Activity:
Interview someone who uses home or industrial automation. Identify which sensors or controllers are used and how they improve efficiency. -
Project Idea:
Build a motion-based room-light controller using an Arduino and a PIR sensor. -
Discussion Topic:
“Which has a greater impact on Bangladesh — industrial automation or home automation?” -
Report Writing:
Write a 300–500-word report on how automation helps reduce electricity usage in Bangladeshi homes.
Key Takeaways
-
Automation merges hardware, software, and data for efficiency and convenience.
-
Smart sensors and controllers are at the core of industrial and home automation.
-
Local innovations show how ICT can solve real-world challenges in Bangladesh.
-
Learning automation empowers students to participate in the Smart Bangladesh vision.
Recent blogs
22 December 2025
7 Min Read