Real-Life Uses of Drones in Bangladesh – From Farming to Photography

Dial Chowdhury
20 October 2025 . 8 Minute Read
Introduction
Drones—officially known as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)—are no longer futuristic machines. In Bangladesh, they have become valuable tools in agriculture, logistics, photography, and public safety. From capturing wedding footage in Dhaka to delivering life-saving medicine to remote char areas, drones are reshaping how we live and work.
This article explores the real-world applications of drones in Bangladesh and connects them to the skills ICT Olympiad students can develop for future innovations, startups, and careers in technology-driven sectors.
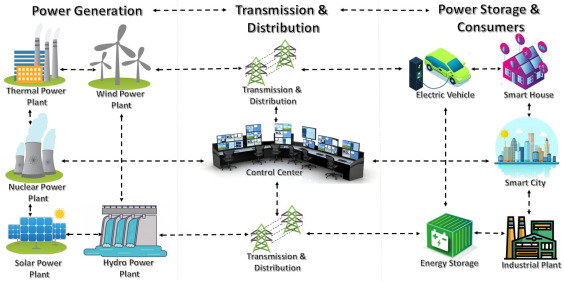
Theoretical Framework: Why Drones Are Useful Across Different Fields
The power of drones lies in their flexibility, automation, and ability to collect real-time data. They combine several key technologies that make them efficient across industries:
| Component | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Control or Autopilot | Operated by a pilot or programmed to fly autonomously | Enables precision and reduces human error |
| Onboard Sensors | Cameras, infrared, environmental sensors | Capture visuals and collect data efficiently |
| GPS & Mapping Tools | Satellite-based navigation | Ensures accurate routing and geolocation |
| Payload Carriers | Lightweight cargo attachments | Carry small packages like seeds, vaccines, or medicine |
When these systems work together, drones become multi-purpose technological tools, supporting everything from farming automation to disaster response.
Tools and Methods Used in Drone Applications
1. Aerial Photography
-
Equipment: High-resolution cameras and stabilizing gimbals
-
Technology: Real-time video streaming, AI for image recognition
-
Applications: Wedding photography, journalism, real estate marketing
2. Delivery Services
-
Equipment: Cargo containers or baskets
-
Technology: GPS navigation and flight control algorithms
-
Example Use: Drone-based delivery of emergency medicine and documents
3. Smart Agriculture
-
Equipment: Spraying nozzles, tanks, NDVI cameras
-
Technology: GPS-based flight mapping, AI-driven crop health monitoring
-
Use Cases: Pesticide spraying, crop growth analysis, soil condition tracking
4. Surveillance and Monitoring
-
Equipment: High-definition and night-vision cameras, thermal sensors
-
Technology: AI-based motion detection and live monitoring systems
-
Use Cases: Crowd control, border surveillance, traffic monitoring
These tools demonstrate how drones act as data-gathering and problem-solving devices, combining engineering, computer science, and automation.
Applications in Bangladesh: Real-World Examples
1. Aerial Photography – Media & Events
Across Dhaka, Sylhet, and Chattogram, drones are widely used in:
-
Wedding videography
-
Television journalism
-
Real estate advertising
? Example: A studio in Dhanmondi uses drone-mounted cameras to capture cultural festivals and concerts, offering cinematic aerial views.
2. Drone Delivery – Emergency Medicine in Rural Areas
In remote regions like Gaibandha, NGOs and startups have tested drone delivery of medical supplies to flood-affected communities.
? Example: A 2023 pilot project successfully delivered emergency medicines to isolated char areas during monsoon floods, reducing response times and saving lives.
3. Smart Agriculture – Farming in Jashore and Rajshahi
Farmers in Jashore and Rajshahi are adopting agricultural drones for:
-
Fertilizer and pesticide spraying
-
Crop health analysis
-
Yield monitoring
? Example: The Bangladeshi startup Agnibot is developing affordable drones for small-scale farmers, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Benefits:
-
Reduces manual labor and exposure to chemicals
-
Enhances spraying accuracy
-
Saves time and resources
4. Surveillance and Public Safety
Government agencies, such as the Dhaka Metropolitan Police (DMP), use drones to monitor large gatherings and ensure public safety.
? Example: During Eid congregations at the National Eidgah, drones provide live aerial monitoring to assist in crowd management and security coordination.
Additionally, disaster response teams in coastal districts deploy drones for cyclone tracking and flood surveillance.
Conclusion: Drones for a Smarter Bangladesh
Drones are no longer just flying gadgets—they are smart systems that empower industries and communities. In Bangladesh, their role in agriculture, healthcare, media, and security demonstrates how innovation can solve real challenges.
For ICT Olympiad Bangladesh students, learning about drones means exploring STEM-integrated skills—from programming and electronics to design and data analytics. You could:
-
Build drone prototypes
-
Develop flight-control software
-
Launch drone-based community projects
By mastering drone technology, you’re contributing to the Smart Bangladesh Vision 2041, where innovation and technology drive national progress.
? Practice Tasks for Students (Class 11–University)
1. Field Research Task
Interview a local photographer, farmer, or journalist using drones.
Prepare a short report describing:
-
Their purpose of using drones
-
Technical challenges they face
2. Idea Development
Design a drone-based solution for a local problem (e.g., mosquito control, flood surveillance, parcel delivery).
Explain how your idea can improve community life.
3. Component Identification Quiz
List and describe the components required for a crop-spraying drone, such as:
-
Frame and rotors
-
GPS system
-
Spray nozzles and pump system
-
Battery and flight controller
Key Takeaways
-
Drones integrate mechanics, electronics, and software for real-world problem-solving.
-
Bangladesh is using drones for farming, medicine delivery, and surveillance.
-
ICT Olympiad students can apply drone knowledge in STEM-based innovation projects.
-
Local startups like Agnibot show how drone technology can support small-scale farmers.
-
Learning drone technology supports the Smart Bangladesh Vision 2041.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. What are the main uses of drones in Bangladesh?
Drones are used in agriculture, aerial photography, delivery services, and surveillance.
Q2. How do drones help in agriculture?
They help farmers spray fertilizers, monitor crops, and analyze soil health efficiently.
Q3. Are drones used by the government in Bangladesh?
Yes. Agencies like the Dhaka Metropolitan Police use drones for surveillance and crowd monitoring.
Q4. Can students learn to build drones in Bangladesh?
Absolutely. Many ICT clubs and robotics programs now include drone assembly and programming.
Q5. How are drones linked to the Smart Bangladesh Vision?
They promote innovation, data-driven decisions, and digital transformation in key sectors.
Recent blogs
22 December 2025
7 Min Read